
Bacterial Structure Plantlet
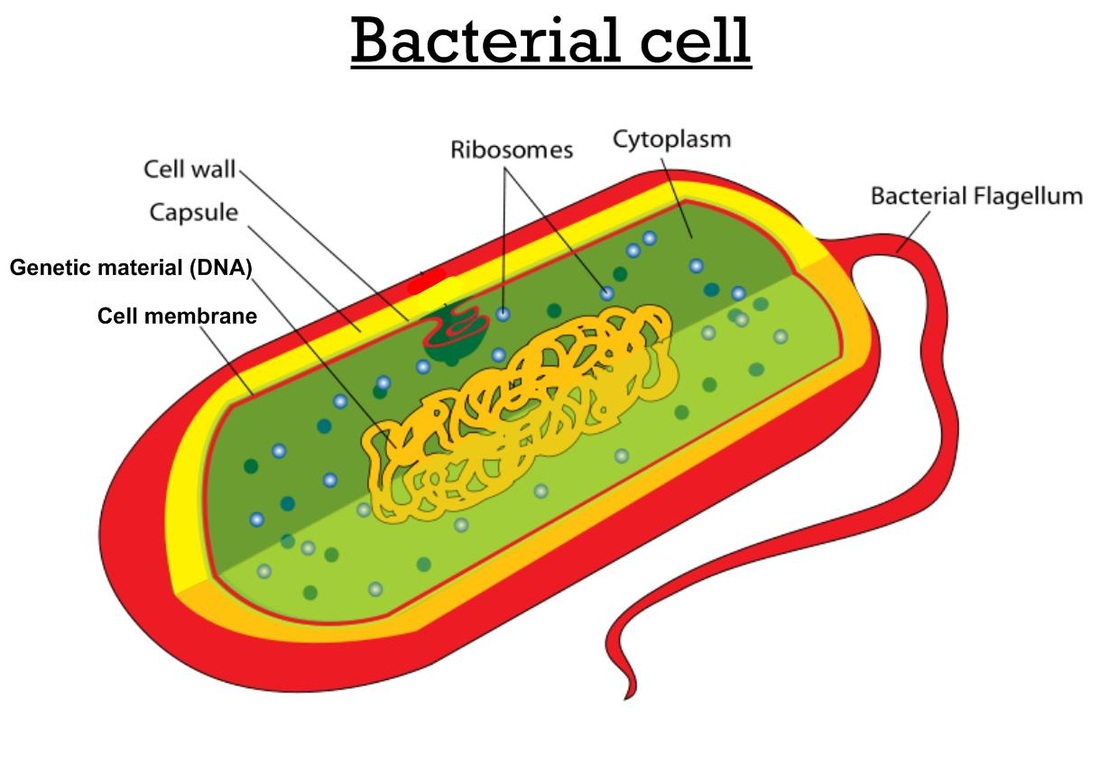
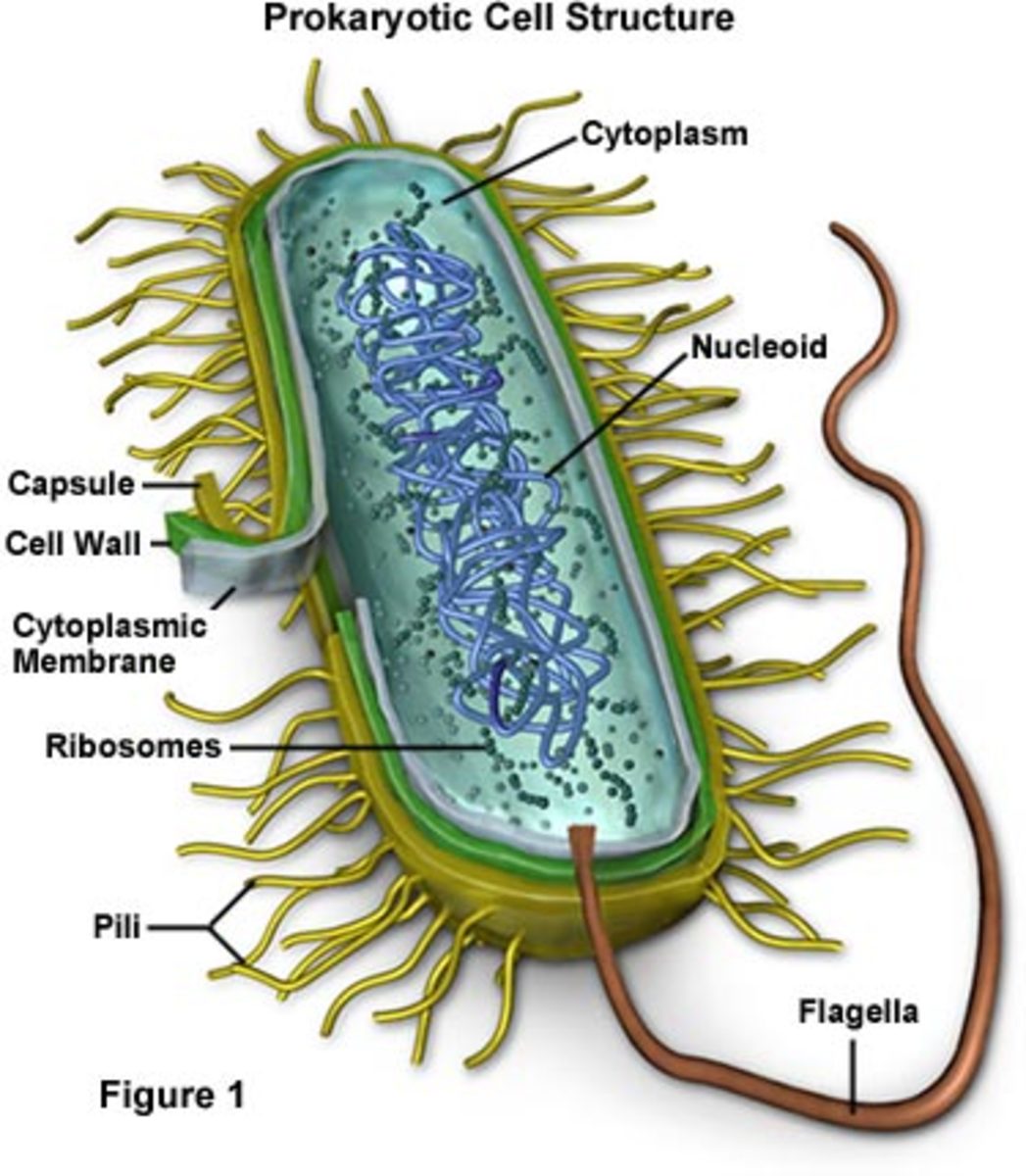
Labelled diagram of a bacterial cell: Cell Capsule: It is a slime layer composed of a thick polysaccharide. It covers the outside of the cell wall. Cell wall: Cell walls of bacteria are made up of glycoprotein murein. Its function is protection. Cell membrane:

Bacterial Structure Plantlet
Figure: Labelled diagram of a typical bacterial cell Cell wall. The thick erect elastic membrane that lies beneath the slime layer outside the bacterial cell is called the cell wall. Its thickness is around 10-25 nm and is made up of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. Usually, the cell wall does not contain cellulose.
Bacteria Ms A Science Online
Biology teaches use that bacteria tend to be unicellular organisms with a peculiar structure. Featuring in this page is an interactive bacteria labelled diagram. It features an annotated diagram with labels to drag and drop at the correct position. This worksheet teaches students the structure of bacteria in a fun way.
Innovic Medical Bacterial Cell Structure
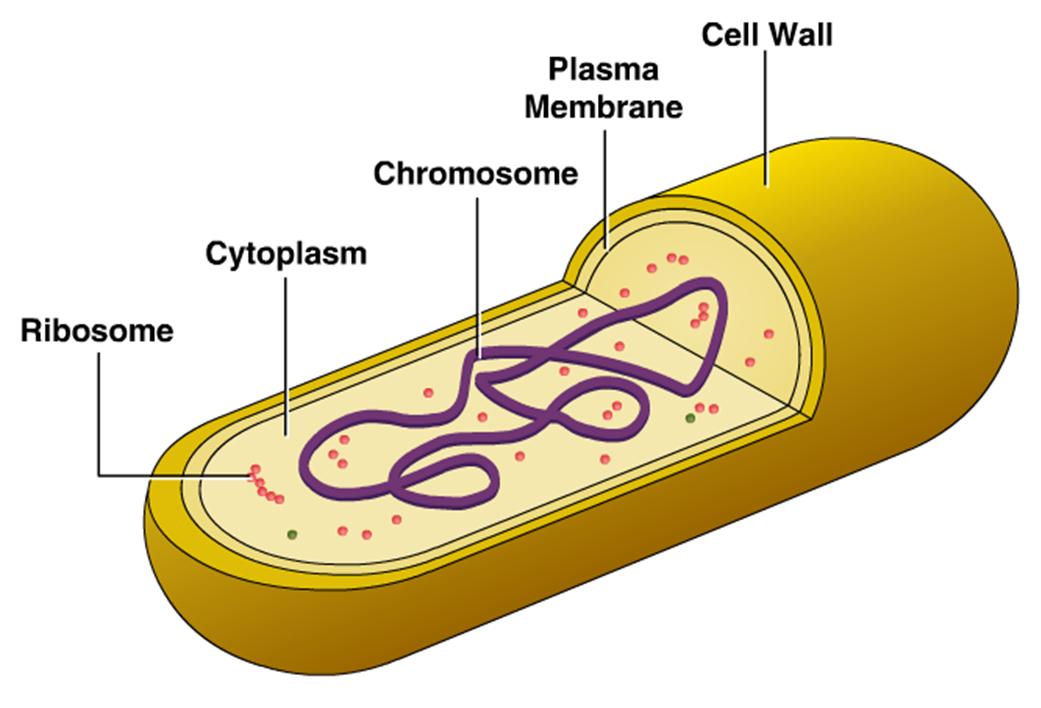
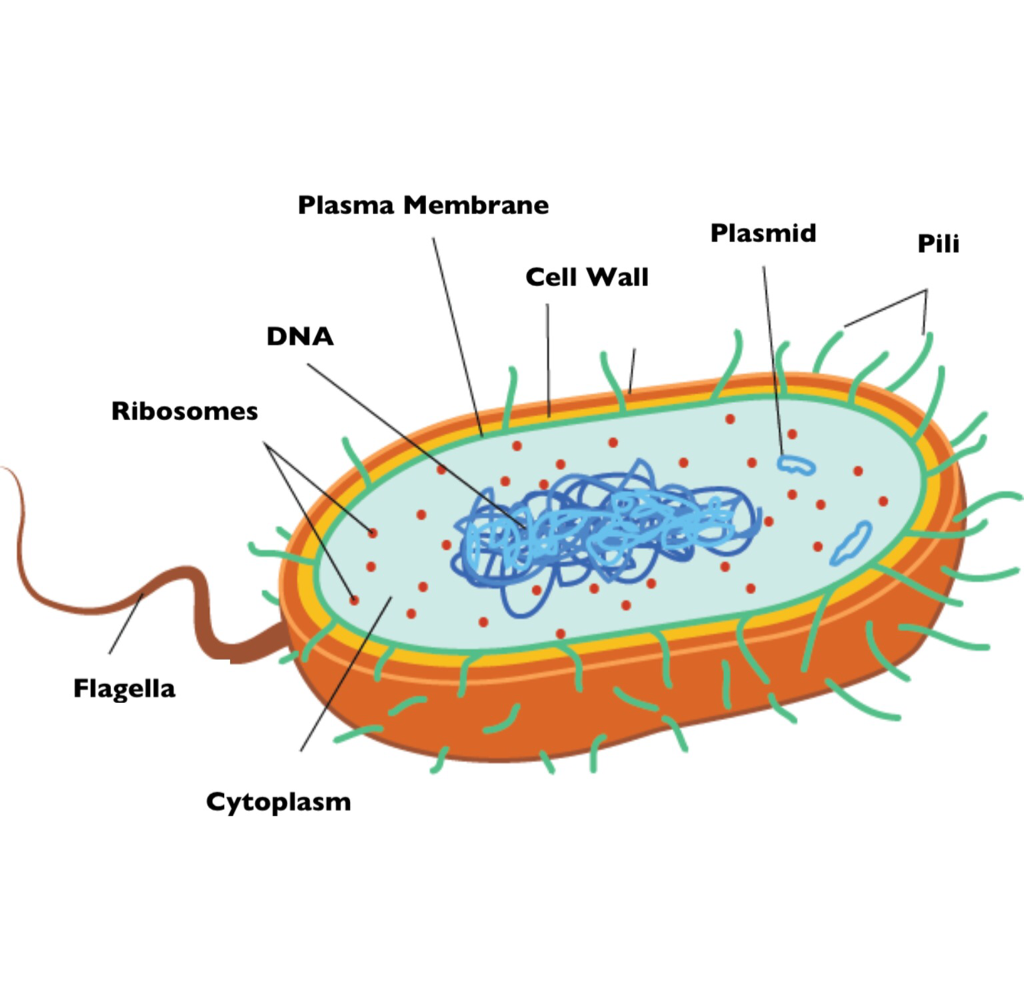
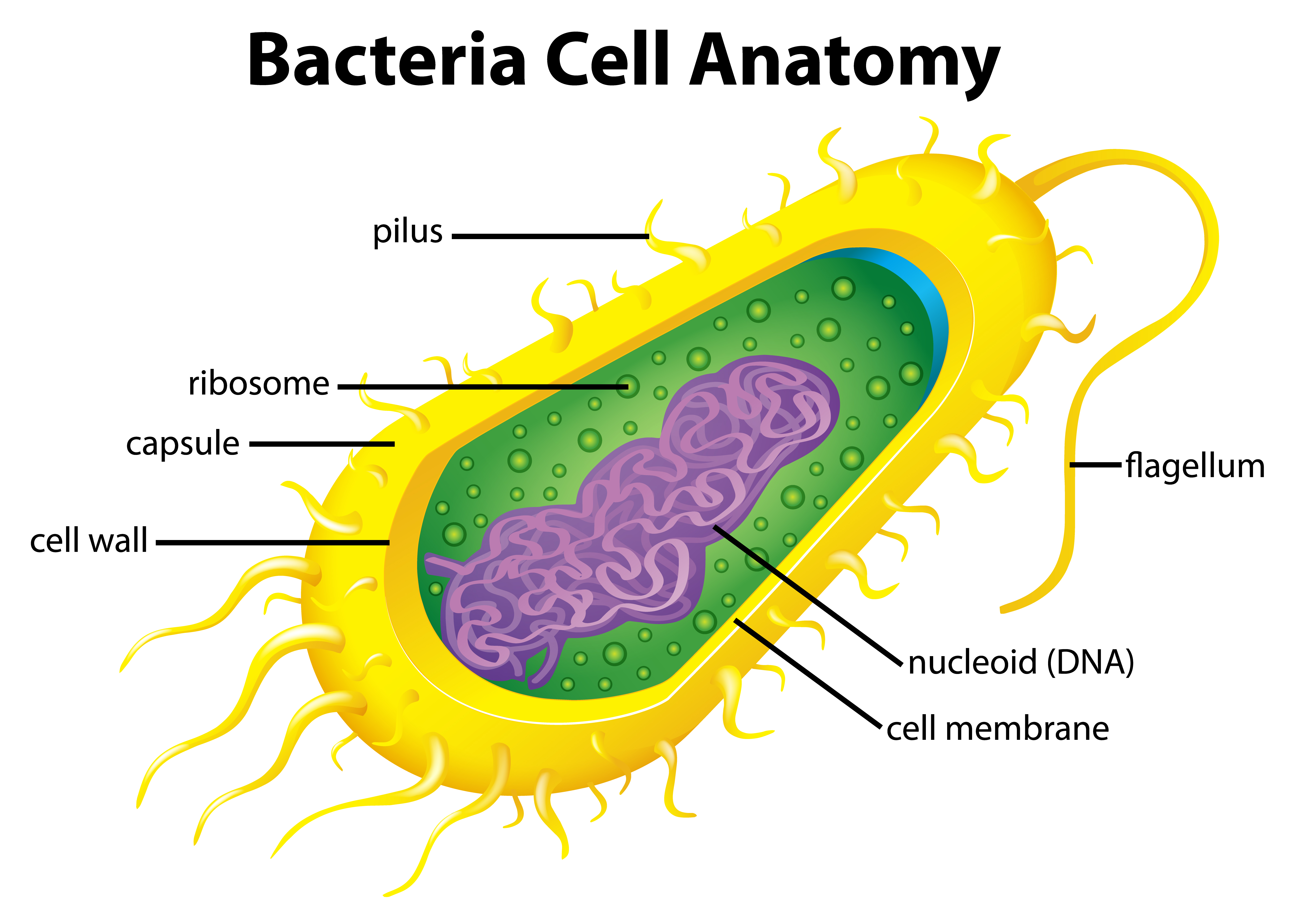
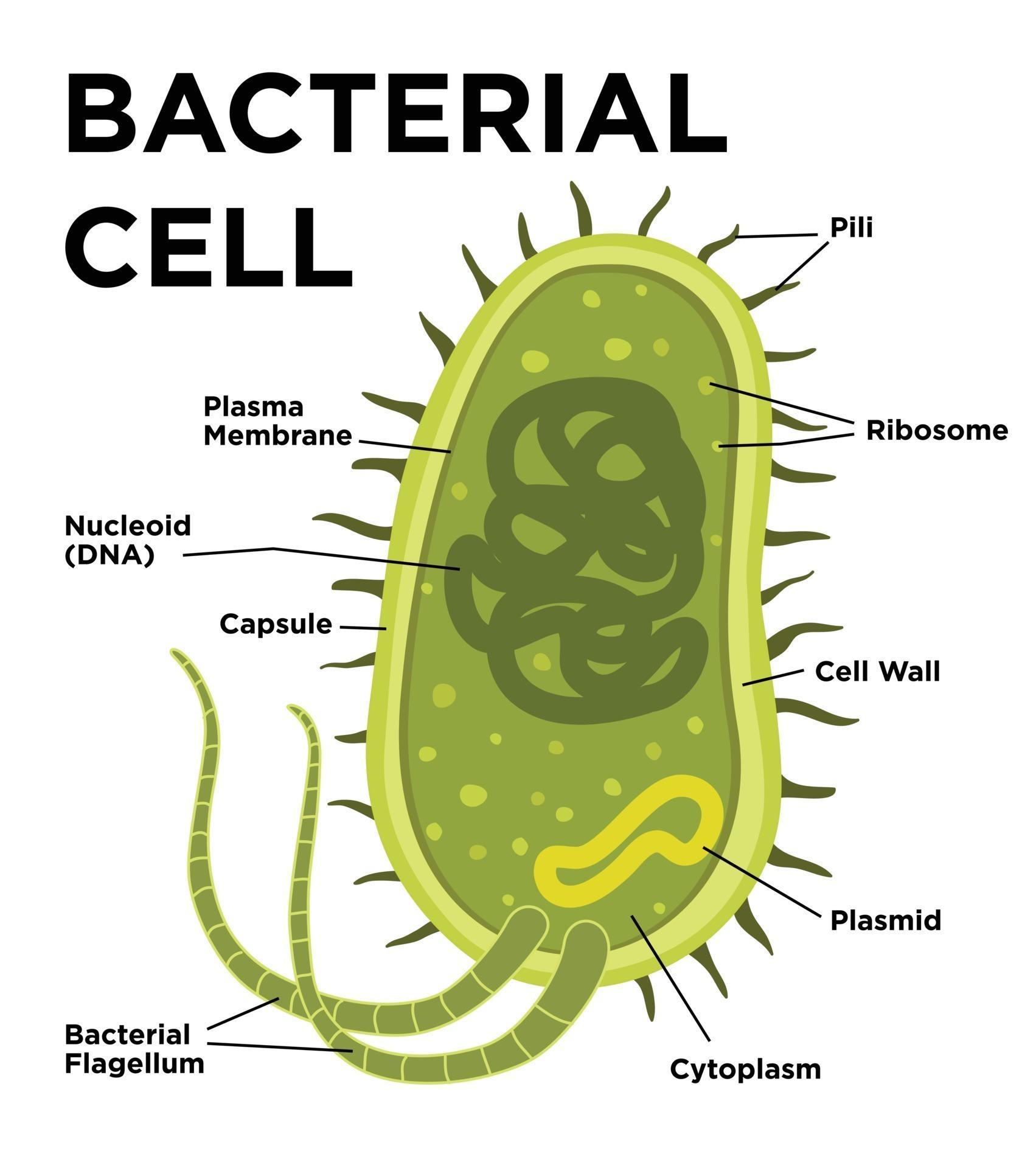
Bacteria Diagram with Labels. Bacterial cells have simpler internal structures like Pilus (plural Pili), Cytoplasm, Ribosomes, Capsule, Cell Wall, Plasma membrane, Plasmid, Nucleoid, Flagellum, etc. Labeled Bacteria diagram. Eukaryotes have been shown to be more recently evolved than prokaryotic microorganisms.
Bacterial structure and morphology by Dr. Shireen Rafiq (RMC)
1.11: Prokaryotic Cells. Distinguish between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells in terms of structure, size, and the types of organisms that have these cell types. Identify structures of bacterial cells in models and diagrams, including details of Gram-positive and Gram-negative cell walls and flagella.
Bacteria Grade 11 Biology Study Guide
The structure of bacteria is known for its simple body design. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles; hence, they are classified as prokaryotic organisms. They are also very versatile organisms, surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions. Such organisms are called extremophiles.

prokaryotic cell bacteria parts
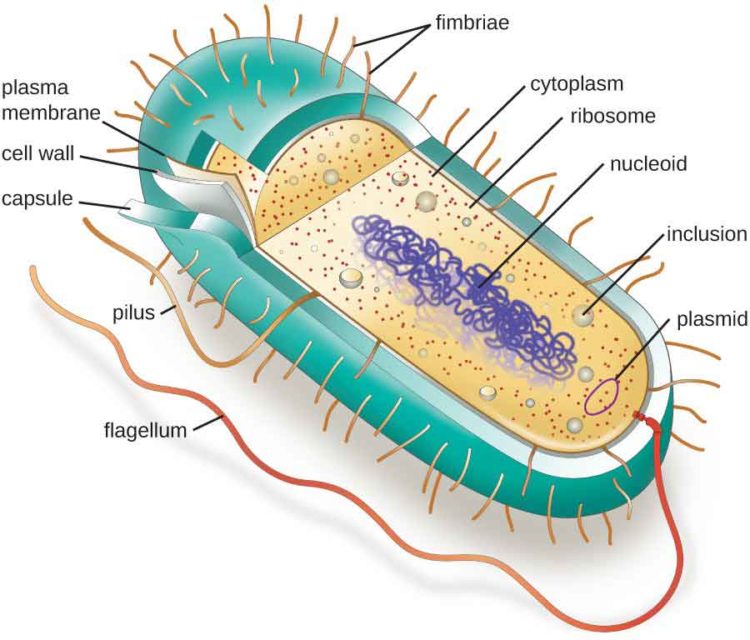
DNA in a nucleus. Plasmids are found in a few simple eukaryotic organisms. Prokaryotic cell (bacterial cell) DNA is a single molecule, found free in the cytoplasm. Additional DNA is found on one.

Bacteria cell anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image
ADVERTISEMENTS: The below mentioned article provides a diagram of bacteria along with additional information as follows:- 1. Occurrence and Distribution of Bacteria 2. Size of Bacteria 3. Forms 4. Staining Bacteria (Gram Reaction). Occurrence and Distribution of Bacteria: The bacteria constitute a highly specialised group of one-celled plants. There are about 2,000 known species. They […]
Bacterial Intracellular Structures That Give Bacteria/Prokaryotes an
In this article we will discuss about the cell structure of bacteria with the help of diagrams. A bacterial cell (Fig. 2.5) shows a typical prokaryotic structure. The cytoplasm is enclosed by three layers, the outermost slime or capsule, the middle cell wall and inner cell membrane. The major cytoplasmic contents are nucleoid, plasmid, ribosome.
Bacteria Cell Vector Art, Icons, and Graphics for Free Download
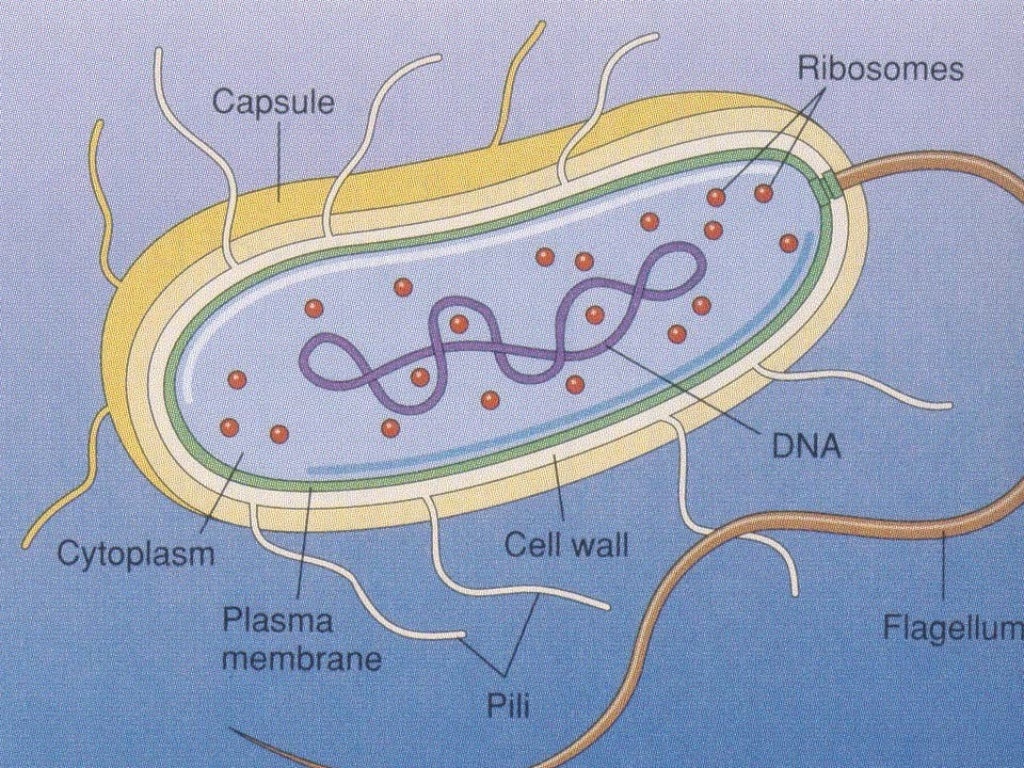
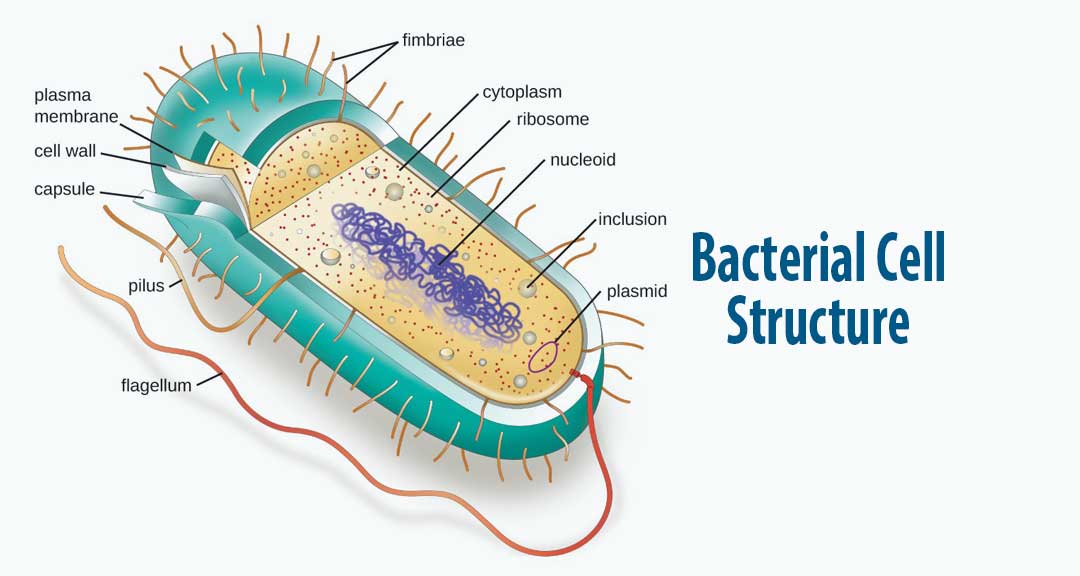
1. A bacterial cell remains surrounded by an outer layer or cell envelope, which consists of two components - a rigid cell wall and beneath it a cytoplasmic membrane or plasma membrane. 2. The cell envelope encloses the protoplasm, made up of the cytoplasm, cytoplasmic inclusions (such as ribosomes, mesosomes, fat globules, inclusion.

bacteria cell diagram labeled simple
3,336 bacteria cell diagram stock photos, 3D objects, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See bacteria cell diagram stock video clips. Structere of a bacterial cell. Diagram. E Coli bacteria micro biological vector illustration cross section labeled diagram. Medical research information poster.

Bacteria Year 12 Human Biology
Cell size. Typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The figure below shows the sizes of prokaryotic, bacterial, and eukaryotic, plant and animal, cells as well as other molecules and organisms on a.
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
This is labelled "Streptococcus pnuemoniae: Causes pneumonia." The second cell resembles a worm. It is about 12 spheres squished together into a curved line. This is labelled "Streptococcus pyogenes: causes Strep Throat." The third cell is four spheres stuck together in a square shape. This is labelled "Micrococcus luteus: causes armpits to stink."
Structure of a typical bacterial cell
These are thin, short filaments (0.1-1.5 μm x 4 to 8 nm) extruding from the cytoplasmic membrane, also called pili. They are made of protein (pilin). It is an outer covering of thin jelly-like material (0.2 μm in width) that surrounds the cell wall. Only some bacterial species possess capsule.
Bacterial cell anatomy in flat style. Vector modern illustration
Bacteria Diagram. Below is the properly labeled diagram of bacteria, showing all the different parts of a bacterial cell. Nutrition in Bacteria. Bacteria exhibit diverse nutritional strategies, allowing them to obtain energy and nutrients in various ways. These strategies can be broadly classified into two categories: Autotrophic Nutrition
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
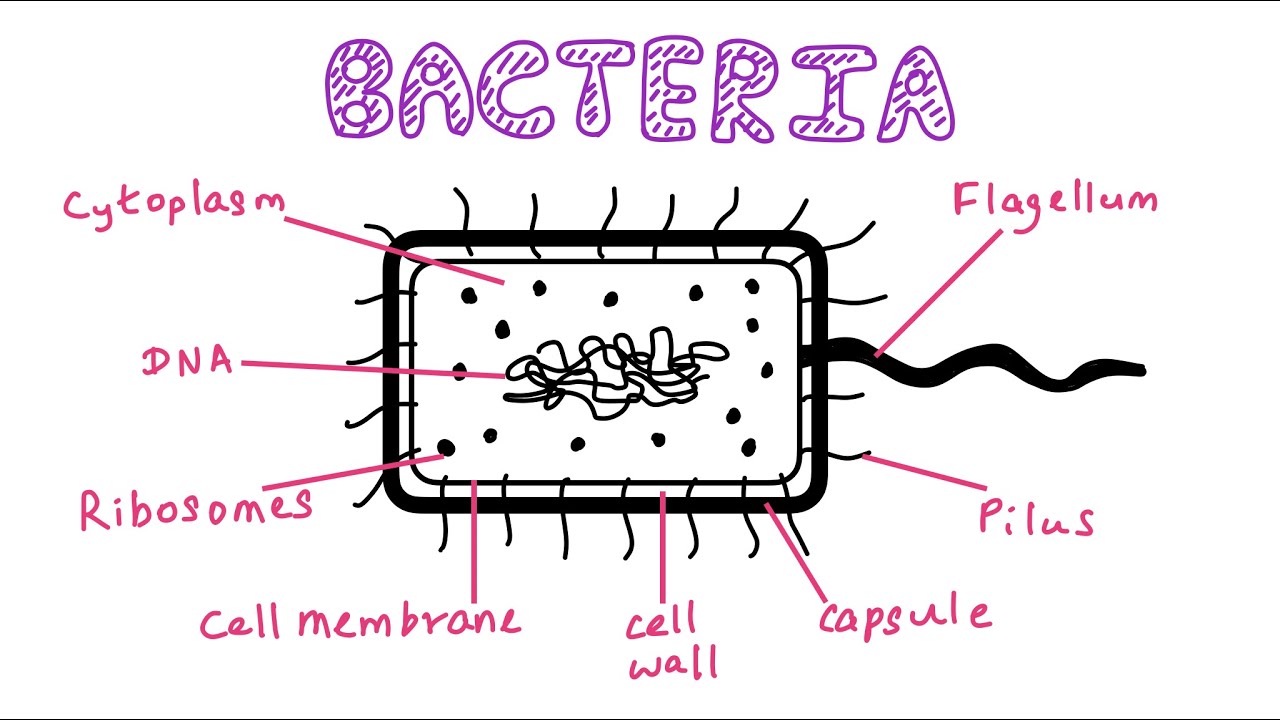
Summary edit. English: A simple diagram of a bacterium, labelled in English. It shows the cytoplasm, nucleoid, cell membrane, cell wall, mitochondria (which bacteria lack), plasmids, flagella, and cell capsule. The SVG code is valid. This diagram was created with an unknown SVG tool.